MySQL InnoDB Introduction
用了 MySQL 这么久,现在才第一次看了下官方关于 InnoDB 的文档
Base
先简单说一些 InnoDB 的特性
- ACID,支持事务 commit 和 rollback
- Row-level Locking
- 聚簇索引(clustered index)
- Foreign Key
Benefits
- 自动 crash recovery
- 用 buffer pool 缓存表和索引的数据
- 可以压缩表和索引
- adaptive hash index,对于
=和IN操作,能缓存常用 pages
Best Practices
- 指定主键或者 auto-increment
- 关闭 autocommit
- 不要使用
LOCK TABLES而是SELECT ... FOR UPDATE锁对应行
Advanced
ACID
Atomicity
Autocommit setting
COMMIT / ROLLBACK
Consistency
- doublewrite buffer
- crash recovery
Isolation
- Autocommit setting
SET ISOLATION LEVEL语句- Locking
Durability
- doublewrite buffer
fsync()system call
其中,Consistency 和 Durability 着重点有点不同,前者是指数据上的一致性,满足相应的约束设置,通过一些策略保证数据在 crash 之后不会丢失或者出现脏数据。后者则是关注与硬件打交道,保证数据库软件上的稳定性。
上述提到的 doublewrite buffer 是一个为了故障恢复的设计。
Before writing pages to the data files,
InnoDBfirst writes them to a storage area called the doublewrite buffer. Only after the write and the flush to the doublewrite buffer have completed, doesInnoDBwrite the pages to their proper positions in the data file.
意思是先写 buffer,然后确认 buffer 没问题再写到对应的磁盘位置。如果中间出现了 crash,就能直接从 buffer 写到对应的文件。需要注意的是,这里的数据单位是 page,这里的 page 也不是 OS 的 page 的概念,而是引擎本身定义的数据单元。
如 InnoDB 默认是 16K,计算校验和也是以 16K 作为单位,但如果系统的 page 大小小于 16K 的话,则意味这有多次写入。如果出现 crash 的情况,只要计算 buffer 和磁盘处的校验和是否一致即可。此外,buffer 的写入是线性的,buffer 到实际的磁盘写入是随机的,所以实际上没有 100% 的性能损耗,更详细的可见 这篇文章。
Multi-Versioning
InnoDB 是一个 multi-versioned 的存储引擎, 保留了修改前的信息,用以并发和事务回滚。实现上,有额外三个字段来支持这个功能
DB_TRX_IDinsert 或者 update 当前行的上一个事务 ID,此外,删除也会有DB_ROLL_PTR指向一个 undo log 记录DB_ROW_ID一个单调递增的 row ID,如果没有指定主键,则会自动创建一个聚簇索引指向这个 ID,否则不会有任何索引引用该 ID
undo log 有两种,一种是 insert undo log,当事务提交之后就可以删除。另一种是 update undo log,与事务生命周期绑定,只有还有事务引用该版本,则会一直保留。如果还有对应的 update undo log 存在,则该行数据则不会实际删除,只有相关事务提交了,update undo log 不在了才会进行删除,这由额外的线程进行 purge 操作。
而对于聚簇索引和二级索引,两者处理逻辑也不同。前者直接在当前记录上更新,后者则不包含隐藏字段,标记删除然后新增记录。如果标记删除后,则通过聚簇索引相关的 undo log 反查去当时版本的记录。
In-Memory Structures
Buffer Pool
The buffer pool is an area in main memory where
InnoDBcaches table and index data as it is accessed. The buffer pool permits frequently used data to be processed directly from memory, which speeds up processing. On dedicated servers, up to 80% of physical memory is often assigned to the buffer pool.
具体实现是基于 LRU 算法的 linked list,以 page 为元素。实现上有 new sublist 和 old sublist 两种。
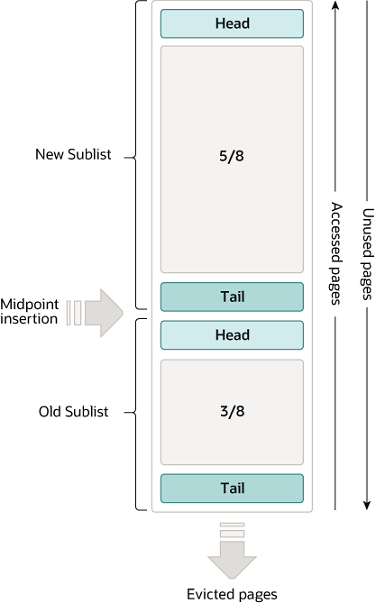
insert 位置设计得挺巧妙,看了解释,触发 insert 有两种情况,一是实际调用 SQL,还有就是 read-ahead 产生的数据。那些用一次的 SQL 就会不断淘汰 old sublist 的元素,而不会影响 new sublist 的元素。
Change Buffer
The change buffer is a special data structure that caches changes to secondary index pages when those pages are not in the buffer pool.
与聚簇索引不同,二级索引的写入很多是无序的,所以如果需要对二级索引的更新需要现在缓存中聚合不然会浪费大量 IO。在闲置或者在 slow shutdown 的过程中,才会将 buffer 中的改动同步到磁盘。
Adaptive Hash Index && Log Buffer
AHI (Adaptive Hash Index) 由引擎本身监控判断如果创建 hash index 会提升速度,才会去创建。其缓存的是 index 和 pages 的关系,其可作用于几乎所有的涉及到 index 使用的场景,如 JOIN,但对 LIKE 的作用则不大。
Log Buffer 用作 redo log 缓存,减少磁盘 IO。
On-Disk Structures
AUTO_INCREMENT
InnoDB 有配置项来针对 auto increment 字段。[innodb_autoinc_lock_mode][3] 有三个选项
- 0 - traditional
- 1 - consecutive
- 2 - interleaved
旧版本 MySQL 用的是 1,MySQL 8.0 用的是 2。这个反映了 8.0 的同步机制从 statement-based replication(SBR) 到 row based replication (RBR)的改变。前者对语句的确定性要求很高,但 auto increment 的字段有可能出现不连续的情况,后者则对此并不敏感。创建表需指定 auto increment 的字段为 primary key 或者 unique key 才行(需要查询其最大值),而常见就是作为表的主键。
目前有几种场景会产生新的记录
- simple insert - 简单的 insert 语句,可以预先得知插入行数
- bulk insert - 不能预先得知插入的行数
- mixed-mode - 插入语句中指定了 auto increment 字段的值和
INSERT ... ON DUPLICATE KEY UPDATE。后者会出现新分配的 auto increment 的值不会被使用的情况
traditional 是有一个表级锁 AUTO-INC 来限制,而锁的使用是针对 insert 语句的,而不是事务,保证了 binary log 的执行顺序,那么就能保证同步之后的数据也是确定的。
consecutive 机制是针对 bulk insert。如果在做 bulk insert 的时候,源表和结果表不一致,则目的表在源表进行第一行查询时上一个 shared lock 之后再上一个 AUTO-INC 锁。如果源表和目的表一致,则在所有的行都查询出来时加上 shared lock 再上一个 AUTO-INC 锁。
如果是 simple insert,则没有 AUTO-INC 锁,而是通过一个 mutex 来获取已知的自增的值。这个 mutex 获取是在资源的阶段,而不是一直持有到语句结束。如果别的事务在使用 bulk insert 则意味着需要等待。目前而言,auto increment 产生的值都是连续的,而在 mixed mode 的情况下,会预先生成多几个值,而用不上的几个就丢失了。
interleaved 机制则是没有表级别的 AUTO-INC 锁。语句可以同时执行,auto increment 的字段则是保证单调递增的生成,所以无法确定语句最后分配的值是多少。
上述三种策略都是针对语句级别,意味着在事务回滚的时候,还是会有空缺的 auto increment 的值。第三种情况性能最好,但不能保证生成的值是连续的。
Index
InnoDB 用 primary key 或者是第一个 unique index 作为 clustered index。每个表只有一个,如果不定义则会默认生成一个,和别的 index 即 secondary index 相比,其性能好很多。clustered index 指向数据的 page 而 secondary index 指向 clustered index,即 secondary index 会多一次 IO 操作。
Tablespaces
system tablespace 是 change buffer 的存储区域,也存放创建于该区域的表和索引。
file-per-table tablespaces 存放一个 InnoDB 表数据和索引。单个文件的实现在管理上非常方便,如果多个表混用一个文件,涉及到文件磁盘空间管理,备份等操作都相对复杂。相对地,做 fsync 操作时,如果一次写入多个表就涉及到多个 fysnc 的调用。
general tablespace 通过 CREATE TABLESPACE xx 来创建,是一个 InnoDB 的 shared tablespace。相比上述的 file-per-table tablespaces,general tablespace 可以定义再 MySQL 的目录之外来做数据管理或者数据备份,也有更好的内存优化来做内存表。
还有如 undo tablespace,temporary tablespace 等在运行时针对特定功能的 tablespace,在实际应用层使用上不会涉及,更多是后续针对实际使用的性能指标来进行微调。
Redo Log and Undo Logs
The redo log is a disk-based data structure used during crash recovery to correct data written by incomplete transactions. During normal operations, the redo log encodes requests to change table data that result from SQL statements or low-level API calls.
Redo Log 是记录准备要去变更数据的 SQL 或者 API。InnoDB 事务中的 A C D 特性就是由 Redo Log 去实现。在故障中恢复时,就是依赖 Redo Log 去将还没持久化的数据写到磁盘中。
Redo Log 不是直接写磁盘,而是写到一个 log buffer 先,然后由 log buffer 再写到磁盘。在 8.0 之前的版本,log buffer 的写入需要先获取一个全局的 mutex 来,8.0 之后改用了一个基于 atomic 的操作来在 log buffer 预分配空间
1 | |
此外还有一个 link buf 来维护 log buffer 到磁盘的写入磁盘的进度,详细细节可见 [这篇文章][4]。log buffer 的写入是需要保证顺序的,每一次写入到 log buffer 则会携带一个自增的 LSN(Log Sequence Number),之后顺序写入到磁盘。写如了 log 之后,后续的实际修改数据或者故障恢复就有了保证。
Undo Logs 相对简单,它记录了需要回滚时用到的旧记录和在多个事务操作过程中需要看修改前的记录的场景。因为仅仅在系统运行时使用,它设计上没有像 Redo Log 那样需要多个 IO 来保证写入,性能上比 Redo Log 好很多。
Locking and Transaction
Shared / Exclusive / Intention Locks
InnoDB 有两种行级别锁
- A shared (S) lock permits the transaction that holds the lock to read a row.
- An exclusive (X) lock permits the transaction that holds the lock to update or delete a row.
对数据读是共享锁,写时是互斥锁。此外还有一个意向锁
- An intention shared lock (IS) indicates that a transaction intends to set a shared lock on individual rows in a table.
- An intention exclusive lock (IX) indicates that a transaction intends to set an exclusive lock on individual rows in a table.
意向锁是表级锁
Before a transaction can acquire a shared lock on a row in a table, it must first acquire an IS lock or stronger on the table.
Before a transaction can acquire an exclusive lock on a row in a table, it must first acquire an IX lock on the table.
它们的关系如下
| * | X | IX | S | IS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| X | Conflict | Conflict | Conflict | Conflict |
| IX | Conflict | Compatible | Conflict | Compatible |
| S | Conflict | Conflict | Compatible | Compatible |
| IS | Conflict | Compatible | Compatible | Compatible |
A lock is granted to a requesting transaction if it is compatible with existing locks, but not if it conflicts with existing locks. A transaction waits until the conflicting existing lock is released. If a lock request conflicts with an existing lock and cannot be granted because it would cause deadlock, an error occurs.
行锁请求前必须先请求对应意向锁,意向锁间不互斥。意向锁是为了更快地判断是否存在互斥的行锁而不用进行全表扫描,如已经申请了 IX 锁,那么 S 锁就申请失败(这个 S 锁前会有一个 IS 锁但不会与 IX 互斥)。意向锁由系统自身进行控制,我们能操作的是显示声明需要用共享锁或者互斥锁。
Record Locks
A record lock is a lock on an index record. For example,
SELECT c1 FROM t WHERE c1 = 10 FOR UPDATE;prevents any other transaction from inserting, updating, or deleting rows where the value oft.c1is10.
SELECT ... FOR UPDATE 会申请一个针对索引的锁,即使没有创建索引也会根据其隐含的聚簇索引来加锁,任何 insert / update / delete 相关记录的操作都会被禁止。
Gap Locks
A gap lock is a lock on a gap between index records, or a lock on the gap before the first or after the last index record.
当隔离级别是 READ COMMITTED 时,gap lock 不会生效。与别的锁不一样, 两个事务可以对同一个范围申请 gap lock,只有插入数据到该范围时 lock 才生效。
Next-Key Locks
A next-key lock is a combination of a record lock on the index record and a gap lock on the gap before the index record.
InnoDB 的共享锁和互斥锁实际上是作用在 index 上的。为了解决 REPEATABLE READ 隔离级别情况下的幻读,在申请锁时,会连同数据索引附近的数据范围也会上锁。而如果是唯一索引,则会降级为 Record Lock。
Insert Intention Locks
插入意向锁是一种由 INSERT 语句带来的锁。插入时在相应索引位置的附近的范围申请一个 index gap lock,如果其它事务同时插入到相同位置则需要等待锁释放。
此外还有一个为地理坐标系数据 Spatial index 设计的 Predicate 锁,这里就不展开说了。在不显示声明使用锁的情况下,不同的隔离级别会有不同的默认锁操作
- READ COMMITTED - 读不加锁,写入加锁,导致事务进行中时读取到别的事务提交的数据
- REPEATABLE READ - 默认的隔离级别,第一次读时生成 snapshot,后续所有的 nonlocking select 都是读取到同一份数据,这部分是 MVCC 在起作用。而如果需要获取最新的数据,则需要
SELECT ... FOR SHARE或者SELECT ... FOR UPDATE来读取,此时则是需要 Next-Key lock 来锁定一个范围,这样就能防止 Phantom Rows(幻读)出现。
Transaction
Isolation Levels
REPEATABLE READ,默认的隔离级别,MVCC 和 locking select 相互作用解决幻读问题。
READ COMMITTED,每一次 nonlocking select 都是最新的数据,显式使用 locking select 也仅仅是 index lock 而不带 gap lock。
READ UNCOMMITTED 则是性能最好的一个,但是几乎不可能在现实中用到,会出现脏读的现象。
SERIALIZABLE 与 REPEATABLE READ 类似。如果 autocommit disabled 则每个 SELECT 都会隐式加上共享锁。如果 autocommit enabled 则每个 SELECT 是个单独的事务,在该隔离等级下,所有事务都是串行执行。
Autocommit, Commit and Rollback
默认情况下,autocommit enabled。没有明确 START TRANSACTION 或者 BEGIN 语句则会自动提交每一个语句。在事务中如果使用 COMMIT 则会将当前改动落盘,即对别的事务可见,即 autocommit disabled 的话,则 locking read 是无效的。
Consistent Nonlocking Reads
A consistent read means that InnoDB uses multi-versioning to present to a query a snapshot of the database at a point in time. The query sees the changes made by transactions that committed before that point of time, and no changes made by later or uncommitted transactions.
在 RR 的隔离等级下,每一次查询相同的数据都是第一次请求时的 snapshot,如果需要查看最新的数据,则需要先 commit 当前的数据或者使用 blocking select。
Deadlocks
A deadlock is a situation where different transactions are unable to proceed because each holds a lock that the other needs. Because both transactions are waiting for a resource to become available, neither ever release the locks it holds.
文中提到的例子
| transaction | A | B |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | SELECT * FROM t WHERE i = 1 FOR SHARE |
|
| 2 | DELETE FROM t WHERE i = 1 |
|
| 3 | DELETE FROM t WHERE i = 1 |
因为事务 A 在 i = 1 上有共享锁,B 申请互斥锁时需要等,之后 A 再申请互斥锁时则形成死锁。当死锁检测开启之后,会尝试回滚或者终止影响行数较小的事务。
避免死锁的方法
- 需要记住,死锁不是问题,程序应该支持重试事务
- 尽量减少事务大小
- 如果业务逻辑上需要很多
SELECT ... FOR UPDATE或者SELECT ... FOR SHARE,也可以考虑 READ COMMITTED 的隔离等级
Replication
Transactions that fail on the source do not affect replication. MySQL replication is based on the binary log where MySQL writes SQL statements that modify data
这里有一个有意思的地方,replica 可以使用 MyISAM 来做引擎,这样一来像外键就没办法生效。如果你有一个表配置了外键的级联删除 DELETE CASCADE 则该表就不会删除关联的数据。不管是 statement-based 还是 row-based 复制也只是能够处理显式更新,而级联删除这种是引擎内部处理就没办法同步了。
Conclusion
其余的如数据压缩,I/O,参数配置等一些章节就选择性跳过了,目前更多地使用像 AWS 的 RDS 也很少接触实际的数据库配置了。个人感觉最有用的是锁和事务相关的介绍,数据写入磁盘的考虑也是很精彩。
References
[3]: https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/8.0/en/innodb-parameters.html#sysvar_innodb_autoinc_lock_mode “innodb_autoinc_lock_mode”
[4]: https://mysqlserverteam.com/mysql-8-0-new-lock-free-scalable-wal-design/ “8.0-wal-design”